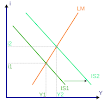
The IS-LM model is a simplified economic framework used to understand how the goods market (represented by the "IS" curve) and the money market (represented by the "LM" curve) interact to determine the overall state of an economy in the short run, essentially showing the relationship between interest rates and output level at equilibrium.
Key points about the IS-LM model:
- "IS" stands for Investment and Savings: This curve shows combinations of interest rates and output where the amount of goods produced (aggregate demand) equals the amount of goods demanded by consumers and businesses, meaning the goods market is in equilibrium.
- "LM" stands for Liquidity and Money: This curve shows combinations of interest rates and output where the demand for money (how much people want to hold in cash) equals the money supply set by the central bank, representing equilibrium in the money market.
- How it works: The IS and LM curves are plotted on a graph with the interest rate on the vertical axis and output (GDP) on the horizontal axis. The point where the two curves intersect represents the equilibrium point in the economy, where both the goods market and money market are balanced.
Key factors that can shift the curves:
- IS curve shifts:
- Government spending: Increased government spending shifts the IS curve right, leading to higher output.
- Consumer confidence: Increased consumer confidence leads to more spending, shifting the IS curve right.
- Investment: Increased business investment shifts the IS curve right.
- LM curve shifts:
- Money supply: Increasing the money supply by the central bank shifts the LM curve right, leading to lower interest rates.
- Demand for money: Increased demand for money (due to factors like uncertainty) shifts the LM curve left, leading to higher interest rates.
Using the IS-LM model:
- Policy analysis: Economists use the IS-LM model to analyze the potential effects of economic policies like fiscal policy (government spending and taxes) and monetary policy (interest rate adjustments) on the economy.
- Understanding economic fluctuations: By examining shifts in the IS and LM curves, policymakers can gain insights into how economic factors like consumer confidence or changes in interest rates might affect output and employment.
Important limitations:
- Simplified assumptions: The IS-LM model is a simplified representation and doesn't account for all complex economic factors like inflation expectations, exchange rates, or external shocks.
- Short-run focus: It is primarily used to analyze short-term economic fluctuations and doesn't fully capture long-run economic growth dynamics.

No comments:
Post a Comment